


Next: 2.2.2 SR spectrometer
Up: 2.2 Experimental setup for
Previous: 2.2 Experimental setup for
The heart of TRIUMF (TRI-Universities Meson Facility)
is a 520 MeV H- cyclotron with a high beam-intensity (140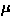 A).
An accelerated proton beam is lead to
a production target made of Graphite or Beryllium. Proton hit the
target-nuclei and create pions via nuclear reactions.
A).
An accelerated proton beam is lead to
a production target made of Graphite or Beryllium. Proton hit the
target-nuclei and create pions via nuclear reactions.
To obtain muons, one must wait for the pions to decay, which
typically takes 26 ns (pion lifetime). To obtain positive muons
(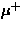 ), one can stop positive pions (
), one can stop positive pions ( ) in the production
target and wait for their decay, because the positive charge of the
pions prevent them from being absorbed into the surrounding nuclei.
These stopped positive pions produce positive muons which are fully
polarized anti-parallel to their momenta (see Fig.6).
These muons are called the `surface muons', because they are emitted
from the surface of the production target. Surface muons have (1)
high spin-polarization (
) in the production
target and wait for their decay, because the positive charge of the
pions prevent them from being absorbed into the surrounding nuclei.
These stopped positive pions produce positive muons which are fully
polarized anti-parallel to their momenta (see Fig.6).
These muons are called the `surface muons', because they are emitted
from the surface of the production target. Surface muons have (1)
high spin-polarization (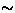 100%), (2) low momentum
(29.8 MeV/c
100%), (2) low momentum
(29.8 MeV/c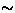 170 mg/cm2 as the stopping range), and (3)
small beam image (a few centimeters in diameter). These features are
all favorable for
170 mg/cm2 as the stopping range), and (3)
small beam image (a few centimeters in diameter). These features are
all favorable for 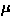 SR measurements. The muon channels M13, M15 and
M20 at TRIUMF are designed to deliver surface muons.
SR measurements. The muon channels M13, M15 and
M20 at TRIUMF are designed to deliver surface muons.
Figure 10:
A schematic view of the M15 beam line at TRIUMF.
 |
Fig.10 shows a schematic view of the M15 muon
channel at TRIUMF. Four dipole magnets (B1-B4) on the
beamline bend the beam and select the momentum of the muons. Quadrupole magnets
(QAQB, Q1-Q17) focus the muon beam. The DC-separators
(SEPARATOR1 and 2) provide crossed electric and magnetic fields
perpendicular to the beamline (see the inset of
Fig.10). This apparatus eliminates positrons
from the muon beam by setting the field ratio (E/B) to
the muon velocity ( ). Secondly, this apparatus can rotate
muon spins away from the momentum direction, by applying higher E and B fields.
All of the surface muon channels at TRIUMF are equipped with at least
one DC-separator; M20 and M15 have the capability to rotate the muon spins
by 90
). Secondly, this apparatus can rotate
muon spins away from the momentum direction, by applying higher E and B fields.
All of the surface muon channels at TRIUMF are equipped with at least
one DC-separator; M20 and M15 have the capability to rotate the muon spins
by 90 .
.



Next: 2.2.2 SR spectrometer
Up: 2.2 Experimental setup for
Previous: 2.2 Experimental setup for
![]() ), one can stop positive pions (
), one can stop positive pions (![]() ) in the production
target and wait for their decay, because the positive charge of the
pions prevent them from being absorbed into the surrounding nuclei.
These stopped positive pions produce positive muons which are fully
polarized anti-parallel to their momenta (see Fig.6).
These muons are called the `surface muons', because they are emitted
from the surface of the production target. Surface muons have (1)
high spin-polarization (
) in the production
target and wait for their decay, because the positive charge of the
pions prevent them from being absorbed into the surrounding nuclei.
These stopped positive pions produce positive muons which are fully
polarized anti-parallel to their momenta (see Fig.6).
These muons are called the `surface muons', because they are emitted
from the surface of the production target. Surface muons have (1)
high spin-polarization (![]() 100%), (2) low momentum
(29.8 MeV/c
100%), (2) low momentum
(29.8 MeV/c![]() 170 mg/cm2 as the stopping range), and (3)
small beam image (a few centimeters in diameter). These features are
all favorable for
170 mg/cm2 as the stopping range), and (3)
small beam image (a few centimeters in diameter). These features are
all favorable for ![]() SR measurements. The muon channels M13, M15 and
M20 at TRIUMF are designed to deliver surface muons.
SR measurements. The muon channels M13, M15 and
M20 at TRIUMF are designed to deliver surface muons.