Up: 7.2 Diffraction of Laser Light by Slits
Previous: 7.2.1 Laser Alignment
- Attach the slide of single slits on a component carrier
and position the assembly midway down the bench.
- Attach the viewing screen to a component carrier
and position it at the right end of the bench.
- Adjust the slit position until the laser beam is incident on the
full width of the slit.
- Observe the diffraction pattern on the screen.
Adjust the screen position if necessary to obtain image clarity.
This is an example of Fresnel diffraction.
- With the slits attached to the side of the component carrier
facing the laser, attach the 48 mm F.L. lens to the other side.
- Move the screen to the focal plane of the lens
(i.e. 48 mm from the center of the lens)
and observe the diffraction pattern.
This is an example of Fraunhofer diffraction.
- Now replace the screen with the linear translator
(with fiber optic probe attached).
Check that the unobstructed laser beam is at the proper level to
be incident on the photometer probe (adjust if necessary).
With the photometer shutter closed,
adjust the translator so that the beam strikes the center of the probe.
Now place the photometer aperture slide on the rear surface
of the translator's analyzer holder so that the 0.1 mm slit
crosses the center of the beam. With this setup, only light incident
on the small slit will be read by the photometer.
- Form another diffraction pattern
and slowly scan the pattern with the translator.
Plot intensity versus position.
Verify that the relative intensity falls off as:

Note: If the laser has not warmed up for at least 1.5 hours,
there may be fluctuations in the beam intensity
due to the expanding laser tube.
- Form the diffraction pattern of multiple slits
and slits of varying sizes and separation.
If the images are too small, magnify them with
a series of lenses.
- Spread the beam of the laser (see Fig. 7.2.2)
and illuminate the special patterns of slide OS-9125.
Observe the diffraction pattern (Fraunhofer and Fresnel).
Attempt to deduce the dimensions of the original aperture arrangement.
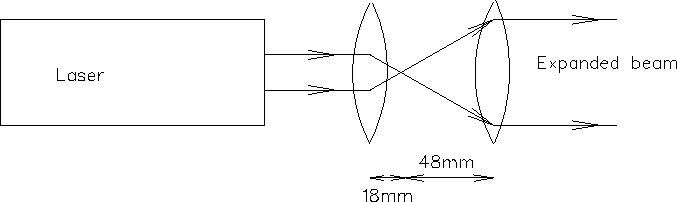
Figure 7.2.2: - Beam spreader arrangement.
Up: 7.2 Diffraction of Laser Light by Slits
Previous: 7.2.1 Laser Alignment


